OOPs is known as “Object Oriented Programming”.OOP is a Programming paradigm or a feature based on the concept of “Objects”. A programming paradigm means way of organizing a program. The two major programming paradigms are:
- Structured Programming paradigm - adopted by C,Pascal
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) paradigm - adopted by C++,Java,C#,VB.NET
Before we move towards OOPs concepts Lets talk a bit about Structured Programming paradigm and it's disadvantages.
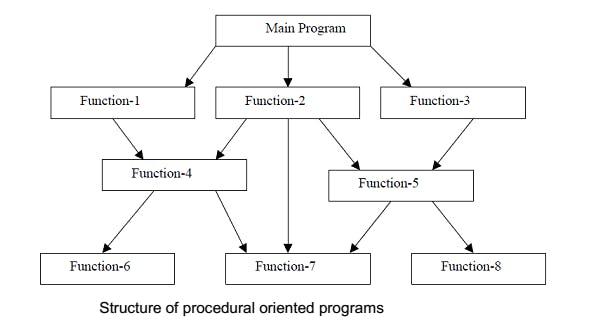
Structured Programming paradigm
- Emphasis on breaking the given task into smaller sub-tasks
- For each sub-task functions are written
- These functions are called directly or indirectly from main()
- No importance given to data, it is just passed from one function to another as required.
Structured Programming in Everyday Life
1. Sequence Execute a list of statements in order.
Example: Baking Bread Add flour. Add salt. Add yeast. Mix. Add water. Knead. Let rise. Bake.
2. Repetition Repeat a block of statements while a condition is true.
Example: Washing Dishes Stack dishes by sink. Fill sink with hot soapy water. While moreDishes Get dish from counter, Wash dish, Put dish in drain rack. End While Wipe off counter. Rinse out sink.
3. Selection Choose at most one action from several alternative conditions.
Example: Sorting Mail Get mail from mailbox. Put mail on table. While moreMailToSort Get piece of mail from table. If pieceIsPersonal Then Read it. ElseIf pieceIsMagazine Then Put in magazine rack. ElseIf pieceIsBill Then Pay it, ElseIf pieceIsJunkMail Then Throw in wastebasket. End If End While
Disadvantages of Structured programming
- The primary components of structured programming - functions and data structures - didn't model the real world problems in a natural way.
- Mechanisms to reuse existing code were limited.
- Maintaining, debugging and upgrading large programs were a difficult task.
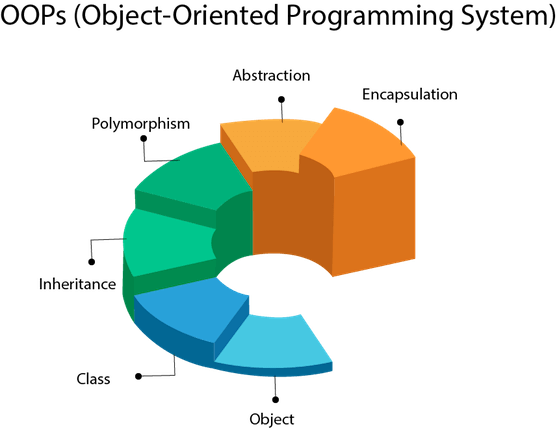
OOPs (Object Oriented Programing)
- Emphasis on identifying objects in a given problem and then writing programs to facilitate interaction between objects
- Objects contain data and functions that can access/manipulate the data
- Equal importance to data as data and functions go together.
- Object-oriented programming aims to implement real-world entities like inheritance, hiding, polymorphism etc. in programming
Characteristics of OOPs
Objects : In Structured Programming a problem is approached by dividing it into functions. Unlike this, in OOPs the problem is divided into objects. Thinking in terms of objects rather than functions make the designing of program easier. For example:
- Employees in a Payroll Processing System
- GUI elements like windows, menus ,icons, etc.
- Elements in games like guns, characters, vehicle, etc.
Classes : The class is one of the Basic concepts of OOPs which is a group of similar entities. t is only a logical component and not the physical entity. A class serves as a blueprint or a plan or a template. It specifies what data and what functions will be included in objects of that type. For example:
- if you had a class called “Expensive Cars” it could have objects like Mercedes, BMW, Toyota, etc.
- if you had an online shopping system it could have objects such as “shopping cart”, “customer”, and “product”
- if you had a house it could have objects like rooms, restrooms, kitchen etc
Inheritance : Inheritance is an important pillar of OOP(Object Oriented Programming). It is the mechanism in java by which one class is allow to inherit the features(fields and methods) of another class.
Let us discuss some of frequent used important terminologies:
- Super Class: The class whose features are inherited is known as superclass(or a base class or a parent class).
- Sub Class: The class that inherits the other class is known as subclass(or a derived class, extended class, or child class). The subclass can add its own fields and methods in addition to the superclass fields and methods.
- Reusability: Inheritance supports the concept of “reusability”, i.e. when we want to create a new class and there is already a class that includes some of the code that we want, we can derive our new class from the existing class. By doing this, we are reusing the fields and methods of the existing class.
Abstraction : Data Abstraction is the property by virtue of which only the essential details are displayed to the user. The trivial or the non-essentials units are not displayed to the user. Ex: A car is viewed as a car rather than its individual components. Data Abstraction may also be defined as the process of identifying only the required characteristics of an object ignoring the irrelevant details. The properties and behaviors of an object differentiate it from other objects of similar type and also help in classifying/grouping the objects. Consider a real-life example of a man driving a car. The man only knows that pressing the accelerators will increase the speed of car or applying brakes will stop the car but he does not know about how on pressing the accelerator the speed is actually increasing, he does not know about the inner mechanism of the car or the implementation of accelerator, brakes etc in the car. This is what abstraction is. In java, abstraction is achieved by interfaces and abstract classes. We can achieve 100% abstraction using interfaces.
Encapsulation : It is defined as the wrapping up of data under a single unit. It is the mechanism that binds together code and the data it manipulates. Another way to think about encapsulation is, it is a protective shield that prevents the data from being accessed by the code outside this shield.
- Technically in encapsulation, the variables or data of a class is hidden from any other class and can be accessed only through any member function of own class in which they are declared.
- As in encapsulation, the data in a class is hidden from other classes, so it is also known as data-hiding.
- Encapsulation can be achieved by Declaring all the variables in the class as private and writing public methods in the class to set and get the values of variables.
-
It refers to the ability of OOPs programming languages to differentiate between entities with the same name efficiently. This is done by Java with the help of the signature and declaration of these entities.
Note: Polymorphism in Java are mainly of 2 types:
- Overloading
- Overriding
