After crawling the images from the web on my previous article Download raw images by keyword using python. Let's discuss downloading videos from the internet by keyword using python in this article. After doing some research, I came up with this site " Pexels" which provides free stock Vimeo videos.
Pexels also provide API for searching videos and photos but in this article, we will use a web scraping using selenium in python.
Planning
Let's understand the approach that we will be using in this article. So, if you check the Pexels website. it will look something similar to this
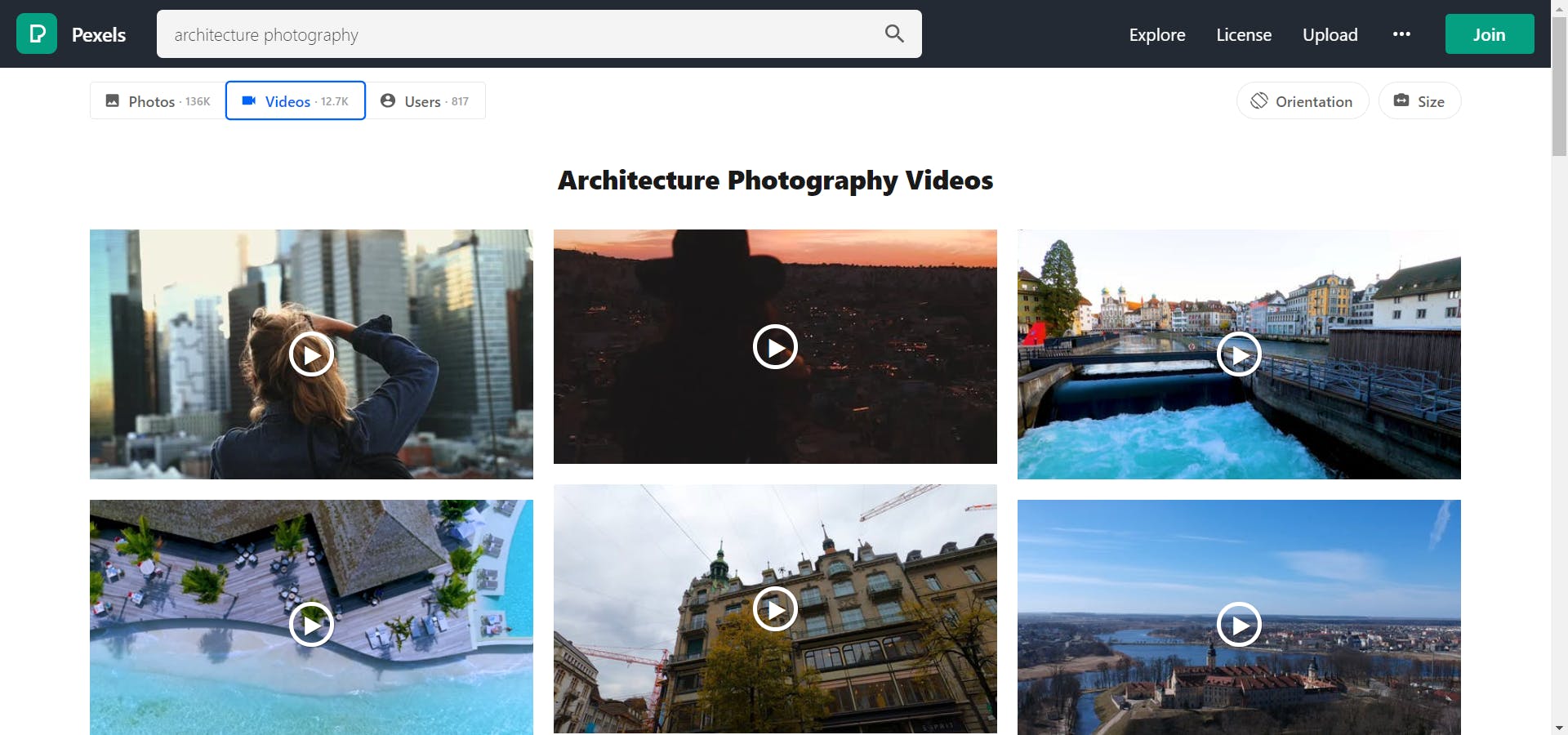
if you search anything in the search bar the URL of the page will also get updated like shown below

This will help us get the images with the keyword. if you see architecture%20photography is nothing but a keyword with URL encoding i.e architecture photography.
now let's check the structure of the website, its element, and video tags. So press F12 or right-click and click on inspect element. it will open up the browser console and check the element tab you will find the HTML structure and there scroll a bit and search for a div with the search__grid class. if you expand that div you will find the structure like this.

Now if you see there is a Video tag with a class called photo-item__video. and inside this tag, you will find the Source tag with type video/mp4. So our goal is to extract the src value of these source tags.
Once we get the URLs we have to transform them into Vimeo URL so that we can download them using vimeo_downloader library in python.
for example, in the above figure, the src contains this URL
https://player.vimeo.com/external/468162983.sd.mp4?s=1f9c036c702fec20f2abb2ae12d3b765ac7afd39&profile_id=139&oauth2_token_id=57447761
we have to grab the id 468162983 from it and generate a new Vimeo Link like this
https://player.vimeo.com/video/468162983
if you check the above link in your browser it will look something like this
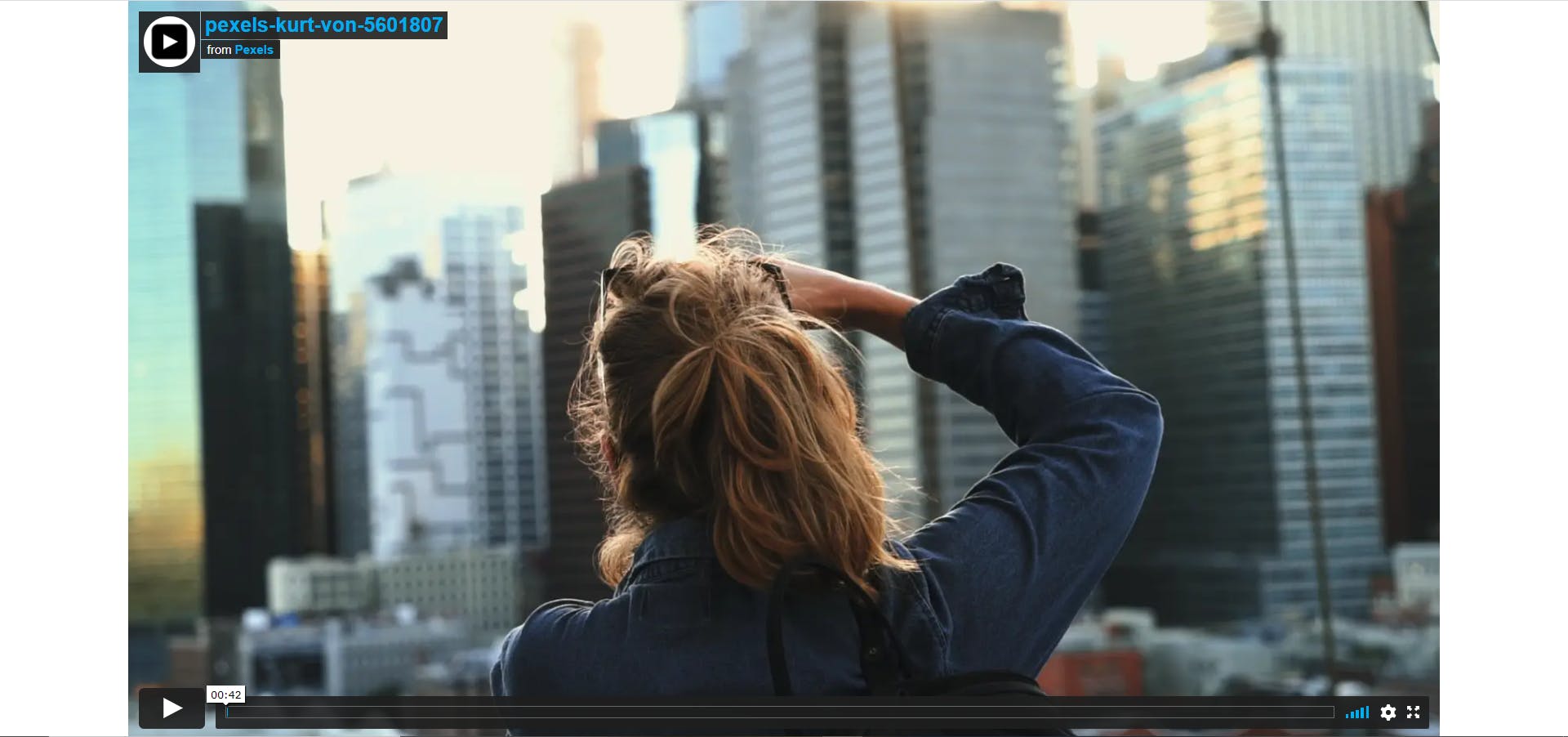

Once we transform the URL we will save it along with the keyword name in an excel sheet. Similarly, we have to grab all the video URL from the page one by one and save it in excel. But keep this in mind, we can't grab all the URLs at once because the website has Lazy loading which means it loads a certain number of posts each time when we scroll the page till 60-70%. that means we have to write a script in such a way it will keep scrolling the page for a certain amount of time. once scrolling is done we have to grab all the video URLs from the page.
Execution
Let's code step by step. First, We will import all the required libraries and learn why we have used them.
#importing required Libraries
import pandas as pd
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
from time import sleep
from vimeo_downloader import Vimeo
import timeit
import urllib
- import pandas as pd - to create a data frame and save the data frame into the excel sheet.
- from selenium import webdriver - Selenium WebDriver is an automated testing framework used for the validation of websites Selenium WebDriver for popular browsers can be downloaded from the links mentioned below:
| Browser | DOWNLOAD LOCATION |
| Firefox | github.com/mozilla/geckodriver/releases |
| Chrome | chromedriver.chromium.org/downloads |
| Internet Explorer | github.com/SeleniumHQ/selenium/wiki/Interne.. |
| Microsoft Edge | developer.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-edg.. |
- from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys - allows pressing keys through keyboard such as ctrl+f, or shift+c+v, etc.
- from time import sleep - Add time delay in the code
- from vimeo_downloader import Vimeo - for downloading the videos.
- import timeit - Measure execution time of small code snippets.
- import urllib - we have used the
urllib.parse.quote&urllib.parse.unquotemodule to encode/decode the URL in a proper format.
Now let's move forward and declare some variables.
#declaring variables
Output_file=r"<path to output directory>\video_urls.xlsx"
xls_content=[]
genres=['fashion portrait']
url='https://www.pexels.com/search/videos/'
path = r'<path to Chrome driver directory>\chromedriver.exe'
here replace <path to output directory> to the absolute path of the directory where you want to store the excel file and replace <path to Chrome driver directory> with the absolute path of the Chrome Driver that you have downloaded from the above table.
Now let's create a if name == "main" function to proceed further.
if __name__ =="__main__":
#setting web driver
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
options.add_argument('--ignore-certificate-errors')
options.add_argument("--test-type")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options,executable_path = path)
# looping through each keyword
for genre in genres:
genre=urllib.parse.quote(genre)
loadpage(driver,genre)
driver.close()
xls_data = pd.DataFrame(xls_content)
xls_data.to_excel(Output_file, engine='xlsxwriter', index=False)
In the above block of code we performed these steps shown below:
- created an object
driverof the chrome `web driver with some options. - Looped through each element in the genres list and did URL encoding in the genre name and passed it as an argument to the function called
loadpagealong with web driver object - closed the driver object with
driver.close()statement. - created the data frame from the list containing a list of video URLs and keywords.
- saved those list of data in an excel sheet.
Now, let's check what is this loadpage function is written for.
#loading genre using webdriver
def loadpage(driver,genre):
driver.get(url+genre) #load the url
sleep(10) # wait for 10 secs so that website loads properly
# scrolling the page for 2 minutes
starttime = timeit.default_timer()
i=0
while i<=120:
driver.find_element_by_tag_name('body').send_keys(Keys.PAGE_DOWN)
sleep(0.5)
i= round(timeit.default_timer() - starttime)
# extract the images from the page
extractingImages(driver,genre)
In this function
- we are loading the URL by using
driver.get(url+genre)and then waits for 10 secs so that the website gets loaded completely. we are sending keypress
PAGE_DOWNto scroll the web page for at least 2 mins to load more videos on the page. As videos are getting loaded from the javascript on scroll. we need to programmatically scroll the page with a delay of 0.5 secs for 2 minutes.starttime = timeit.default_timer() i=0 while i<=120: driver.find_element_by_tag_name('body').send_keys(Keys.PAGE_DOWN) sleep(0.5) i= round(timeit.default_timer() - starttime)where
starttimecontains the time at which we started scrolling and we keep on scrolling until we get the difference of the current time and start time greater than 120 secs i.e 2 minsthen we call the extractingImages with driver and genre as arguments.
Let's define the function extractingImages and see how can we extract images.
def extractingImages(driver,genre):
print(f"Extracting {genre} Video URL after 10 secs....")
sleep(10) # let it load the post properly
images = driver.find_elements_by_tag_name('source')
for image in images:
src=image.get_attribute('src')
vlink=src.split(".sd.mp4")[0].replace("https://player.vimeo.com/external/","https://player.vimeo.com/video/")
temp={}
temp['Genre']=(url+genre).split('/')[-1].replace("%20"," ").upper()
temp['Image URL']=vlink
xls_content.append(temp)
download_vimeo(vlink,url,genre)
- at the starting, we are delaying the code by 10 secs to let the webpage load its contains properly.
- then we are finding the
sourcetag from the website content and looping all matched results to extract thesrcattribute value from it. - we are transforming the URL to the desired URL as discussed in our planning stage.
- next, we are creating a dictionary for each URL found along with the keyword and stored it in a list. so that we can save the records in the excel sheet under the main block.
- we have called another function named
download_vimeoby passing the video link, page URL, and genre to download the videos.
Let's write the download_vimeo function and see how videos are getting downloaded from the links.
def download_vimeo(vimeo_url,embedded_on,genre):
v = Vimeo(vimeo_url, embedded_on)
stream = v.streams # List of available streams of different quality
# >> [Stream(240p), Stream(360p), Stream(540p), Stream(720p), Stream(1080p)]
filename=urllib.parse.unquote(genre)+"-"+vimeo_url.split('/')[-1]
# Download best stream
stream[-1].download(download_directory = 'video', filename = filename)
- In the above function we created an object of
Vimeoclass defined invimeo_downloaderpackage. - listed all the available stream data of different quality from
v.streamsand stored it in a variable calledstream. - Now we are creating a filename by un-quoting the genre and by concatenating it with the id extracted from the video URL.
for example,
filename='Food photography'+"-"+"511722602"i.eFood photography-511722602 - Now we are fetching the best available quality from last index from stream variable i.e
stream[-1]and calls the download function with arguments like folder path and filename. It will download the fileFood photography-511722602.mp4in folder namevideounder the current working directory. Like this, it will download all the files from the extracted video links.
Now let's check the output of the script when we execute it.
- it will open up a browser window and loads the content by keep scrolling for 2 mins.
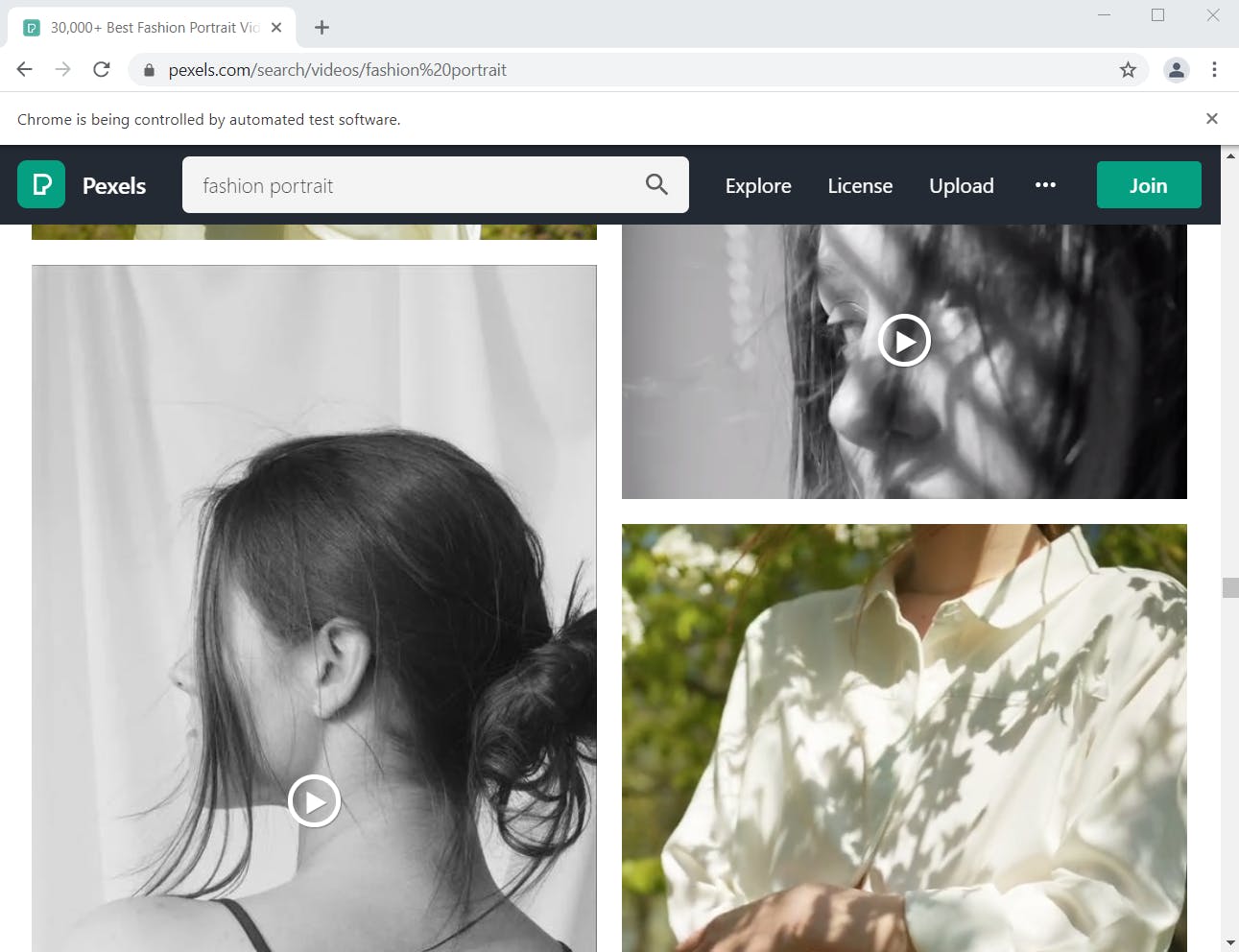
- once it is done with the scrolling it will start downloading all the videos from the links
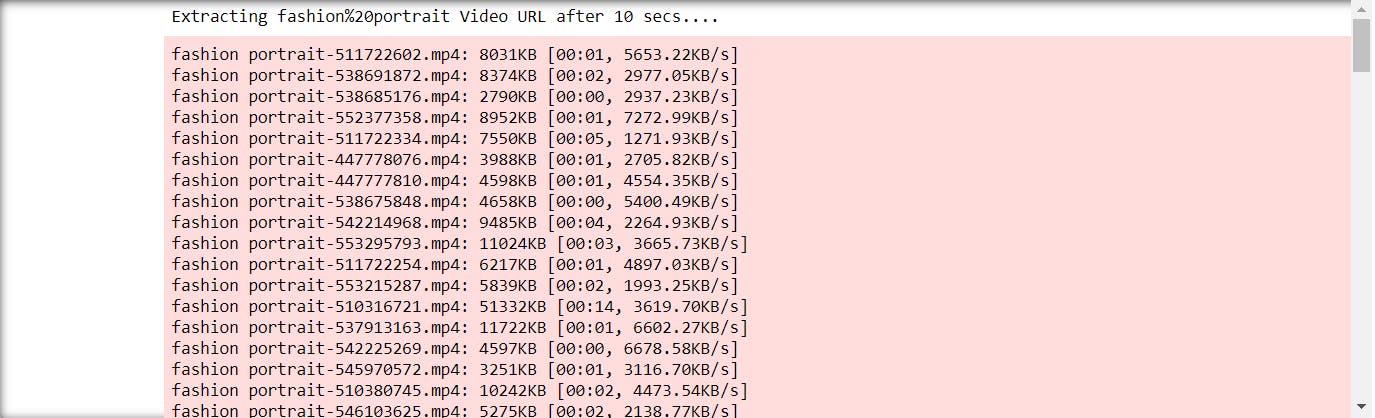
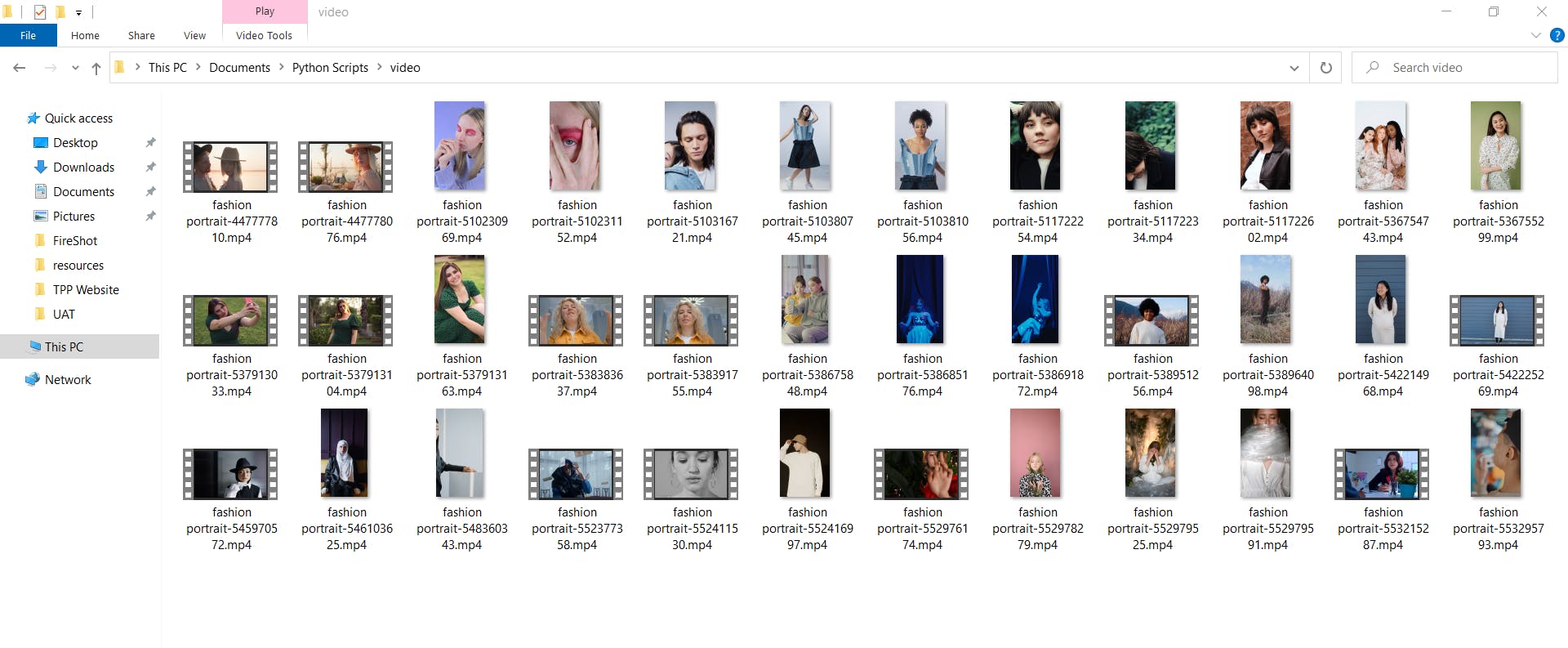
- you can check the
videofolder for the downloaded videos which will look something like this.
- finally, it will generate the excel sheet with the list of files and genres as shown below.
Bonus points
your downloaded file count will depend on the number of videos loaded on the webpage so you can increase or decrease the scrolling duration to control the file counts.
More the duration of scroll more videos it can download and more the time it will take.
you can download multiple types of videos all you have to do is just add the keywords in the
genreslist in the script.scripts allows to opt for downloading the videos if you just want the list then just comment the
download_vimeofunction inside theextractImagesfunction.
You can find the source code of this article from my Github Repository.
You can also download HD images using python. if you want to learn how then check my previous article Download RAW Images by keyword using Python. and if you want to learn more about How to do anything in python then just subscribe to my newsletter. you will get the notification automatically whenever I post a new article to my blog.
I hope you learned something new today from this article. if yes, then please give it a reaction and also give a star to my repository.
Chao!!
.
